private hospitals
6623 Views
Risks and Side Effects of Weight Loss Injections, and Tips Before Using Them
Posted By Pharmacist Mais Hassan |
2025-07-30
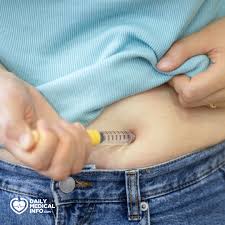
Normally, when we eat, the body produces hormones that stimulate the release of insulin, reduce appetite, and slow the emptying of the stomach to increase feelings of fullness. Weight loss injections work by stimulating the release of these hormones, which in turn helps reduce appetite and the amount of food consumed, supporting weight loss.
There are several pharmaceutical formulations used in weight loss injections, the most well-known include:
• Liraglutide
• Semaglutide
• Tirzepatide
The side effects and risks of weight loss injections vary. Some are mild and common, while others are serious and require medical attention and discontinuation of the drug. Here is a breakdown:
Serious Risks and Side Effects of Weight Loss Injections
Using weight loss injections may be associated with rare but serious side effects, such as:
• Severe allergic reactions, with symptoms like swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing or swallowing, dizziness or fainting, and skin rash.
• Pancreatitis, presenting as nausea, vomiting, severe upper abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, and an increased heart rate.
• Gallbladder issues, requiring immediate medical attention if symptoms like fever, heartburn, upper abdominal pain (possibly radiating to the back), yellowing of the skin or eyes, and clay-colored stools appear.
• Low blood sugar, especially when combined with other diabetes medications. Symptoms include headache, dizziness, hunger, sweating, blurred vision, shaking, and a rapid heartbeat—seek medical help immediately if these occur.
• Kidney problems, including decreased or absent urination, fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling of the feet or ankles.
• Thyroid tumors, including thyroid cancer. All three injection types mentioned above carry a warning due to their association with medullary thyroid carcinoma, as observed in animal studies. It is not yet confirmed if this risk applies to humans.
• Stomach flu (viral gastroenteritis), with symptoms like stomach cramps, vomiting, and watery or bloody diarrhea.
• Mental health concerns, including depression and suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Any changes in thoughts, mood, or behavior should be reported to a doctor immediately.
• Other risks, such as increased or irregular heart rate and vision problems or blurriness.
Risks and Side Effects of Weight Loss Injections in the Elderly
Weight gain in older adults is associated with increased risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, strokes, diabetes, and cancer. This may lead them to use weight loss injections, especially since they may struggle with other methods like exercise.
However, using weight loss injections in older adults comes with specific risks:
• More intense side effects like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are more common and severe in adults over 65, potentially worsening other health conditions.
• Close kidney function monitoring is essential, as older adults are more prone to acute kidney failure, especially if they already have conditions like chronic kidney disease or high blood pressure.
• Muscle loss occurs faster in older adults, particularly with rapid weight loss, increasing their risk of falls and fractures. This can be mitigated by maintaining physical activity and regular exercise.
Groups Prohibited from Using Weight Loss Injections
The following groups should not use weight loss injections due to a higher risk of serious side effects:
• Individuals with personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
• Individuals with a personal or family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2).
• Those already taking other weight loss medications, especially from the same drug class.
• Individuals with diabetic ketoacidosis.
• Those with allergies to any components of the injections.
• Pregnant women.
Groups That Must Consult a Doctor Before Using Weight Loss Injections
Certain individuals with specific medical conditions must consult a doctor before using weight loss injections, including:
• People with digestive issues, especially indigestion.
• Those with current or past problems in the kidneys, liver, pancreas, or gallbladder.
• Individuals with heart problems.
• People with vision issues or diabetic retinopathy.
• Those suffering from depression.
• Anyone planning pregnancy or currently breastfeeding.
• Individuals with a personal or family history of diabetic eye disease.
Alternatives to Weight Loss Injections
There are many effective weight loss methods that can be used instead of injections, reducing health risks. The most important of these include:
• Reducing intake of added sugars and carbohydrates.
• Exercising regularly, such as cardio, resistance training, or other workouts.
• Increasing protein and fiber intake, which helps burn calories, reduce appetite, and prolong feelings of fullness.
• Avoiding processed foods, which tend to be high in fats, sugars, and additives.
• Drinking adequate water, which helps burn calories and may reduce calorie intake.
• Intermittent fasting, which limits the eating window and helps reduce calorie consumption.
• Eating slowly, which can lead to consuming less food overall.
• Consuming probiotics, which may reduce fat absorption and suppress appetite.
Medical Advice
Weight loss injections come with many risks and potential side effects—some of which can be severe and may require discontinuation. To avoid the harms and dangers of weight loss injections, it is recommended to first try other weight loss methods. If injections are necessary, always follow your doctor’s instructions and consult them if you experience any adverse effects or side effects.

comments
No Comments